Compose Options
Learn how to compose Knowledge Stacks
Composing resources initiates the process of preparing your files for retrieval-based AI interactions. When you compose, each resource is parsed and broken down into meaningful chunks, then transformed into vector representations using an embedding model. These vectors are stored in a searchable index, enabling the system to quickly retrieve relevant context during a prompt.
This step is essential for making your documents usable in Knowledge Stacks and ensuring accurate, context-aware responses from the AI.
You can configure compose settings at the resource level and at the composition process level.
Resource Compose Advanced Options Aurum Perk
When adding new resources under files, folders, notes, and YouTube links, additional configuration options will be available under the ellipsis menu.
Configuration capabilities depend on resource upload types.
Load Modes
Select how a file will be loaded during Knowledge Stack compositions. For file uploads, there are three options you can choose from.
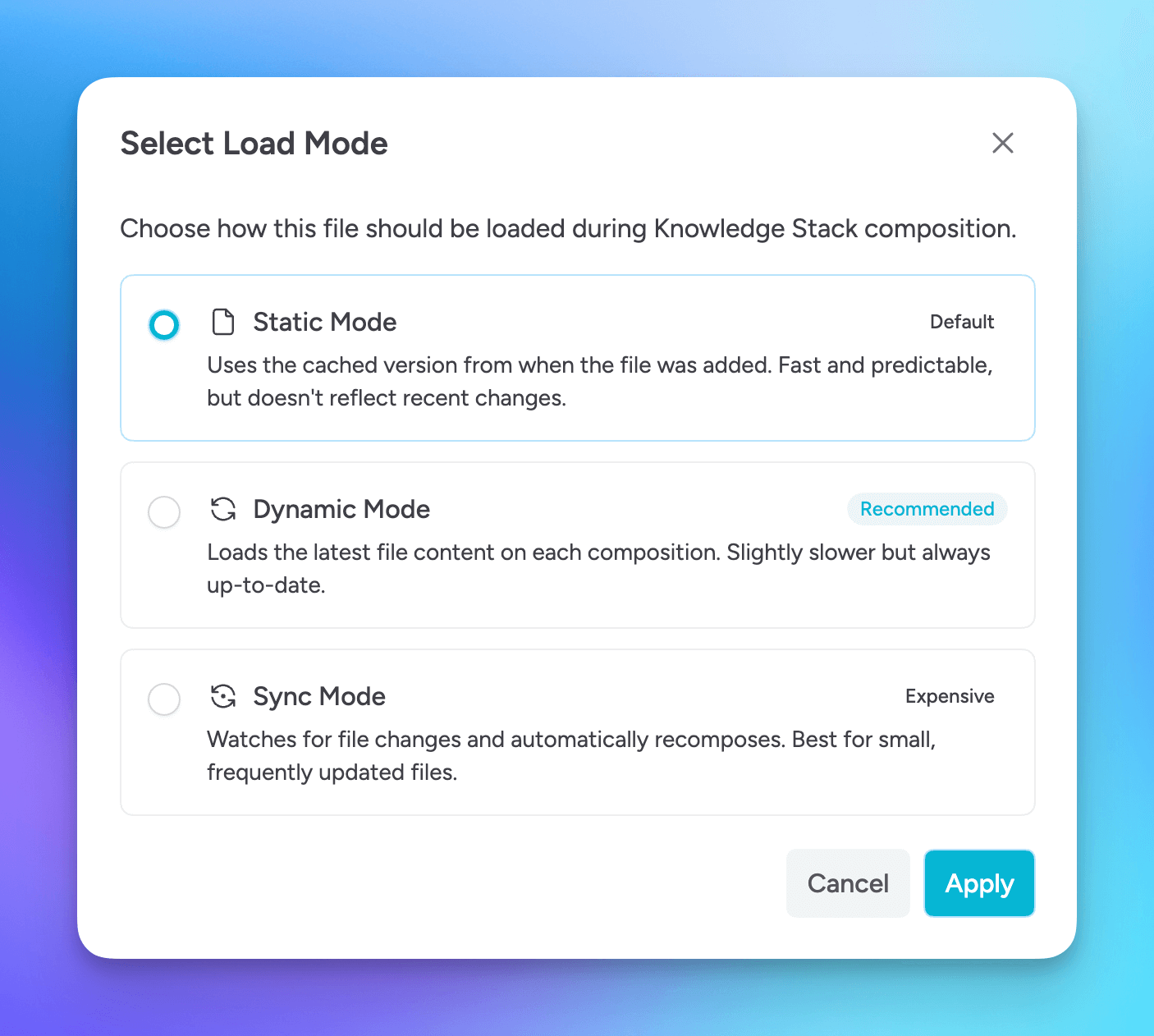
Static Mode
Uses the cached version from when the file was added. Fast and predictable, but doesn't reflect recent changes.
Use this option for source files that are not likely to modified.
This is the default mode for files added to Knowledge Stacks.
Dynamic Mode
Loads the latest file content on each composition. Slightly slower but always up-to-date.
Use this option if you modify source files, want the latest to be included in new compositions, but you are not concerned about the Knowledge Stack having latest information and are okay with manually re-composing.
Sync Mode
Watches for file changes and automatically recomposes. Best for small, frequently updated files.
Use this option if you want the Knowledge Stack to automatically be re-composed when launching Msty and Msty detects that there is a change to a file that is configured for sync mode.
After marking a file for sync mode, you will need to Start Sync Mode from the Knowledge Stack menu in order to watch for file changes and to automatically re-compose the stack.
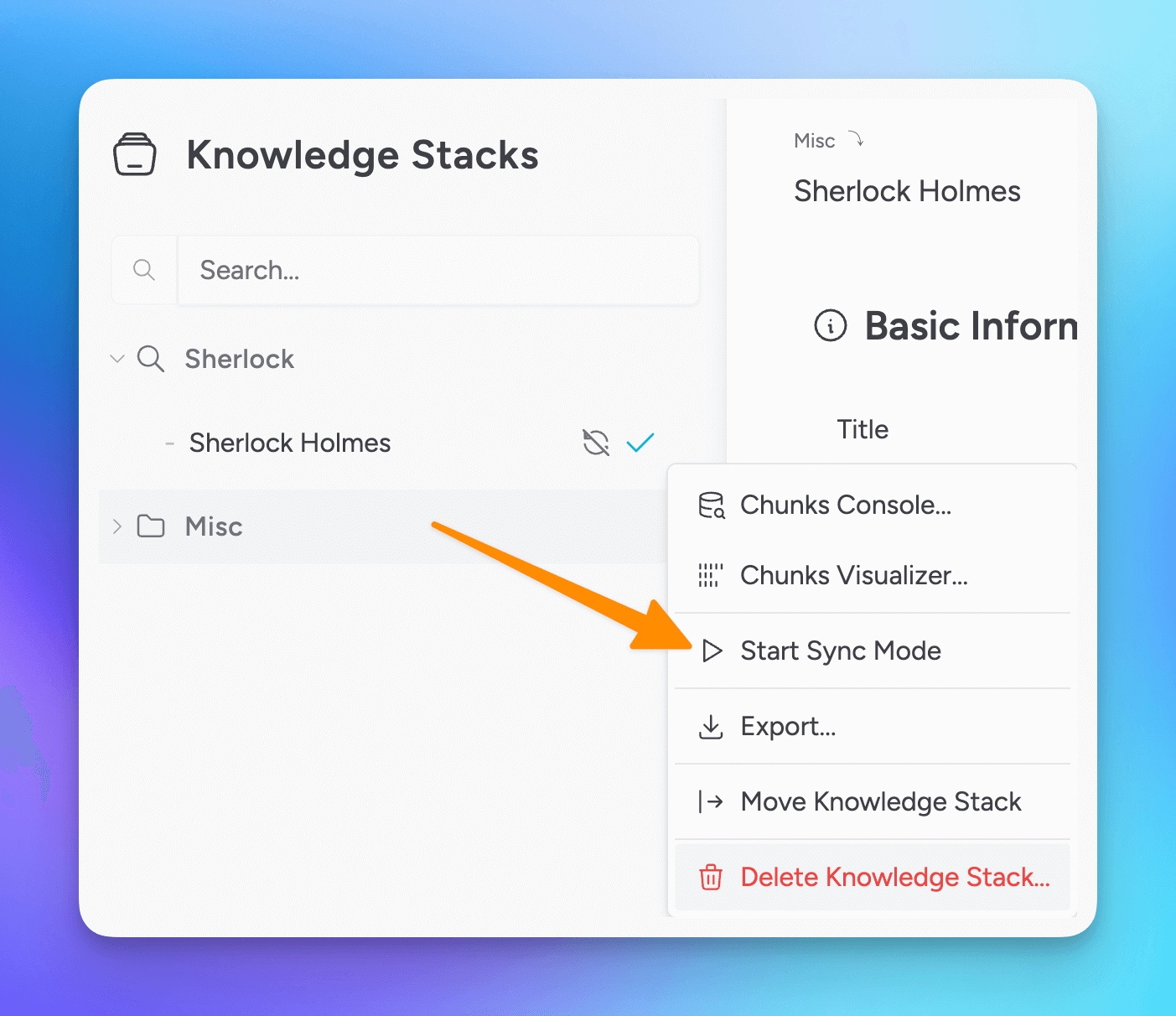
Sync Mode can be expensive in terms of your local resources and processing if files update frequently.
Mark for Reprocessing
Marking a resource for reprocessing will process only those marked resources when clicking Compose.
Ignore for Retrieval
Select Ignore for Retrieval to prevent a resource from being queryable. This is helpful as you perfect your Knowledge Stacks.
Lock a Resource
You can either temporarily or permanently lock a resource.
Temporarily locking a resource will exclude the file during re-composing. However, the resource from it's last composition will be included in query results.
Permanently locking a file is irreversible and will lock the composed resource forever - until deletion.
Use Permanent Lock only if you know you will never update the source file in the future.
If you import a Knowledge Stack, the resources in that imported stack are by default permanently locked. This is because the source files are assumed to not be on your machine and only the vectorized database for the stack is being imported.
Compose Settings
In the Compose Settings area, you can configure the how the Knowledge Stack is composed.
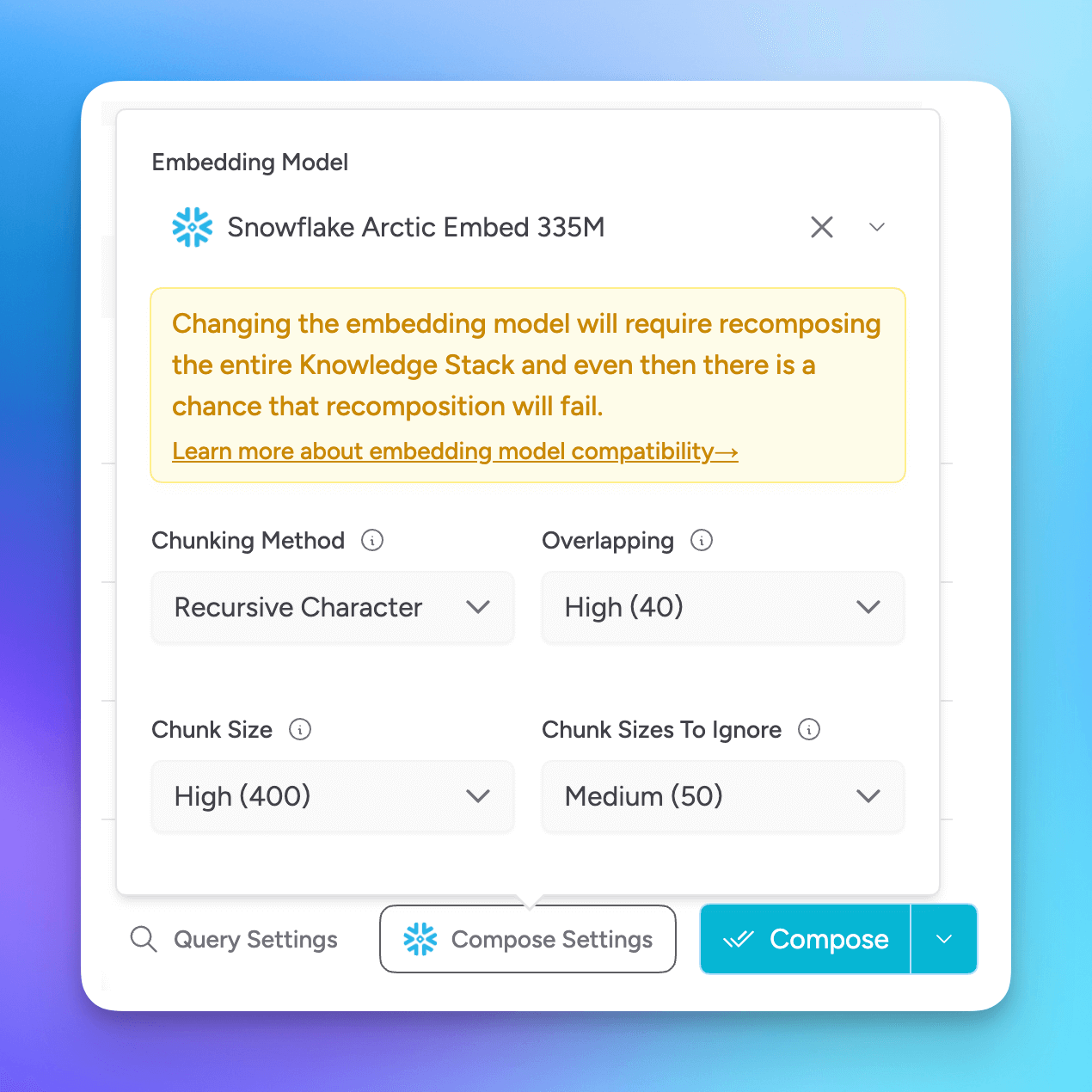
Embedding Model
Msty uses gte-tiny by default, but you can change it to any other embedding model available in your Msty App. You can find an embedding model in Model Hub > Local AI Models.
Some embedding models outperform others by better capturing semantic meaning, understanding context, and generalizing across domains. High-quality models improve retrieval accuracy by generating more meaningful vector representations of text.
When choosing an embedding model, look for strong retrieval performance, domain relevance, efficiency (in size and speed), and compatibility with your deployment setup.
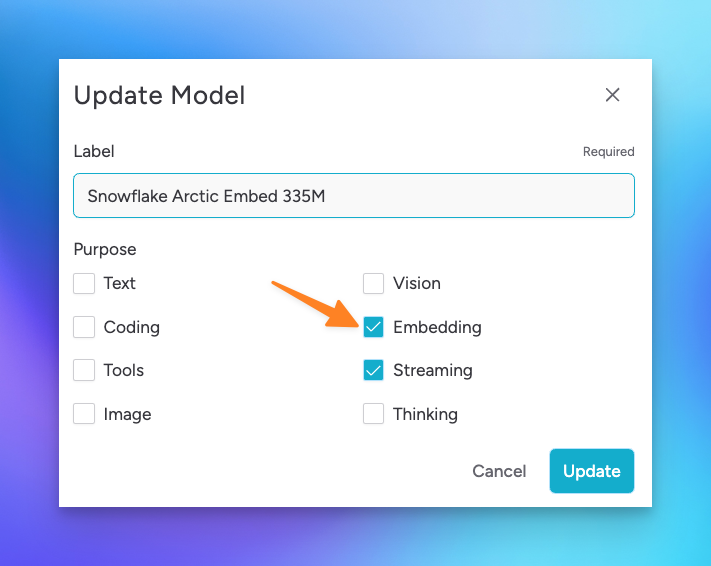
For an embedding model to display as a selectable option, ensure the model has Embedding enabled as a purpose. To check this, select the update model icon from either the model selection list or from the installed local models section in Model Hub.
Chunking Method
Chunking is the process of breaking down large documents into smaller, manageable pieces (or "chunks") to make them suitable for vectorization and retrieval. Each chunk is typically a few hundred words and is designed to preserve context while fitting within token limits of embedding and language models. Effective chunking ensures that relevant information can be retrieved accurately, improving the quality of responses.
Choose how you want to split your content into chunks.
Options include:
- Recursive Character: Splits text into chunks based on character count.
- Sentence: Splits text into chunks based on sentence boundaries.
Overlapping
Configure how much overlap you want between chunks.
This configuration is available when Chunking Method is set to Recursive Character.
Chunk Size
Set the maximum size for each chunk. Smaller chunks may improve search accuracy but can increase processing time and token usage.
Chunk Size to Ignore
Specify chunk sizes that should be ignored during processing. Useful for excluding very small or very large chunks that may not be relevant.
Compose
When you are ready to compose, select the Compose button.
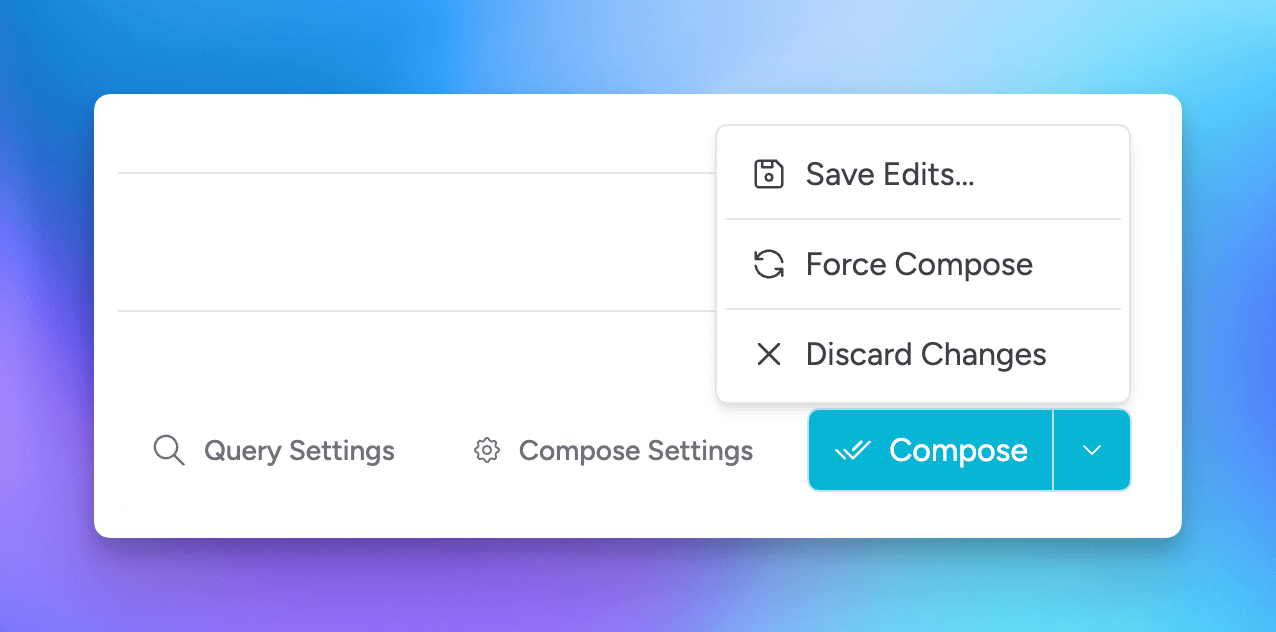
If you haven't made any changes to compose configurations, and want to re-compose, select the Force Compose option.