Tools
Empower Msty Studio with tools in your toolbox
The Toolbox allows for seamless communication with tools installed on your local machine or a remote one. These tools can interact with various data sources, perform file operations, and connect to repositories like GitHub, further empowering Msty Studio.
This is Msty Studio's implementation of Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Msty Studio supports local MCP server that run on your machine as well as remote MCP servers that can be connect to over Streamable HTTP.
Please note the SSE protocol has been deprecated in favor of Streamable HTTP for remote MCP server connections. Studio's implementation came after the deprecation, and as such, SSE is not supported. However, you can use a local proxy such as mcp-remote to connect to SSE-based MCP servers if needed.
To utilize the Toolbox features with Msty Studio Web, you must have Studio Web connected to Studio Desktop using Remote Connections or Sidecar.
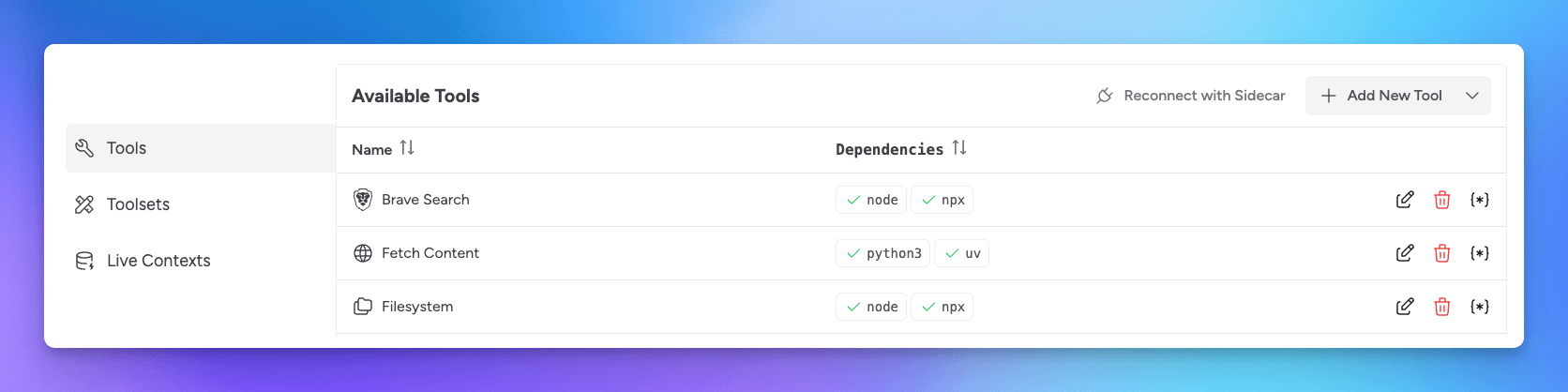
Import Default Tools
Please note that default tools as well as any tool you add are not created, tested, nor maintained by Msty. We are merely providing a platform to use these and allowing to import them as a convenience. PLEASE USE THEM AT YOUR OWN RISK. Msty is not responsible for any issues that may arise from using these tools. Also, for support, please reach out to the tool's author.
To get started, you can select the option to Import Default Tools. Please keep in mind these tools are not created nor maintained by Msty team and are meant to provide a starting point.
Add A New Tool
Select Add New Tool to add a new tool to your toolbox. This will open a new window where you can define the tool's name, configuration, and notes.
- Select HTTP for remote MCP servers setup for streamable HTTP and tools or STDIO / JSON for local MCP servers and tools.
- If HTTP is selected, enter the MCP Server URL endpoint. Also, enter any Authentication and Headers needed to connect to the MCP server.
- If STDIO / JSON is selected, enter the Tool Configuration in JSON format.
The configuration should be a valid JSON object. Here is an example configuration for a MYSQL tool.
Take note of the command, which identifies dependency programs such as Python, UV, Node, and NPX for examples. These programs must be installed on your local machine in order for the tool to run.
If using the above example, then also take note of the variables in the mustache brackets. These are the variables that will be passed to the tool when it is ran. You can use these variables in your tool configuration to make it more dynamic. You will be able to define variables in the following steps.
- Optionally, enter Notes to help you remember the purpose of the tool and any other information you may need to remember
- Give the tool a unique Name
- Select Add to add the tool to your toolbox
Set Tool's Default Parameters
To set default parameters for a tool, select the asterisk (*) icon next to the tool name. This will open a window where you can define the tool's parameters.
Here, you can add Custom Arguments and set Environment Variables that may be needed for the tool to run, such as directory paths, endpoints, API keys, and so on.
There is also a Tool Console where you can test the tool with different parameters.
Install Dependencies
Most tools will require dependencies - such as Node, NPX, and Python - to be installed on your local machine in order to properly run.
For Node installations - at this time, we recommend installing using Volta to manage installing Node and NPX. Mac users may use Homebrew. We do not recommend using NVM. If using NVM, you may need to uninstall and use Volta instead.
To check which package manager you used to install Node, run the following command in your terminal and take note of the directory path.
If installed under NVM directory, then you'll likely need reinstall using a recommended package manager.
If you are running into issues with dependencies not showing as available, click on Sidecar and then select View Logs to see if there are any helpful error messages.